1.LSTM
Table of Contents
1.RNN의 한계
2.LSTM 개념
3.Pytorch 내의 Parameter 설명
4.Pytorch LSTM 구현 튜토리얼
1. RNN의 한계
- Recurrent: 이전에서 온 정보(메모리) + 현재 입력 같이 고려
- 바로 직전이 아니라 그 전 데이터도 필요함
- 단순히 이전 문장만 고려하는 게 아니라 한참 이전에 있는 문장도 고려해야함 -> 현재 내용을 올바르게 유추하기 위해
- longer term dependencies를 고려해야 함 -> 이로 인해 LSTM이 나옴
[스탠다드 RNN]


- 스탠다드 RNN
- 새로운 입력(x(t-1))이 들어오면 이전 값을 0으로 초기화해서 같이 넣어서 네트워크 A로 들어가게 함 -> 이 둘을 합쳐서 output (h(t-1))을 만들고 이걸 다시 다음 input으로 넣음
- 이전 정보와 현재 정보를 취합(concat)한 걸로 뉴럴넷에 들어가서 output이 됨
2.LSTM의 개념
- long term dependency를 잡기 위해서는 훨씬 더 복잡해짐
- short term까지 둘다 잡는 구조임
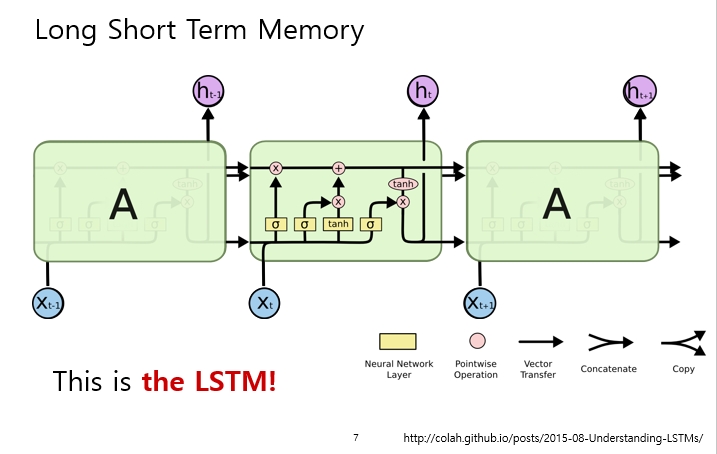
1) 노랑색 박스: 뉴럴 넷 레이어
2) 동그라미: point wise operation: 12개에 12개면 각각을 12 dimension 만큼 곱해서 더하는 것
3) → : vector transfer
4) 선이 합해지면: concat
5) 선이 나눠지면 : copy
(1) 초록색:
이전 정보가 100 dim이고 input이 100 dim이면 concat하면 200 dim이 됨
(2) 주황색:
200 dim에서 100dim으로 가는 network가 됨
[LSTM 전체적인 구조]

1) Input X(t):
- t번째 시간의 단어가 들어감
2) Cell state:
- 절대로 밖으로
빠져나가지 않음. 흘러가는 친구
3) Hidden state:
- 이전 출력
4) Forget Gate, Input Gate, Output Gate
- Gate가 총 3가지로 있고, 이게 잘 조합이 되어서 Long term & Short term을 둘 다 잘 고려하게 됨
- Core는 Cell state: 일종의 컨베이어 벨트 같은 것으로 지금까지의 정보를 잘 취합해서 cell state로 잘 흘러감

- 시그마 -> x는 정보를 여닫는 Gate 역할을 함
[GATE 설명]
(1) Foget Gate
- Decide what information we’re going to throw away from the cell state
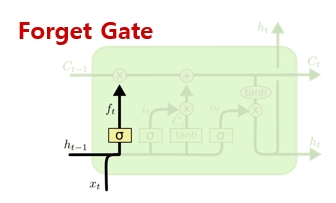


- Forget Gate의 입력: 이전 output(h(t-1))과 현재 입력(x(t))
- Forget Gate의 출력: cell state로 넘어가는게 아니라 cell state로 넝어가는 어떤 값이 나옴 sigmoid로 0~1 값
- Forget Gate의 출력f(t)의 dim이 100 dim(주황)이고, 이전 cell state (c(t))값이 100 dim(초록)을 곱함
-
각각의 dim마다 forget gate 값들이 곱해짐, forget gate은 sigmoid로 0~1
- forget gate가 1이면 이전 cell state가 1로 다 넘어옴
- cell state의 어떤 값을 버릴지를 결정하는 것
2) Input Gate
- Decide what new information we’re going to store in the cell state

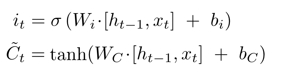
- C(t) 틸다 입력: 이전 output(h(t-1))과 현재 입력(x(t))의 네트워크.
-
C(t) 틸다 출력: tanh(-1~1), 현재 cell state의 candidate
-
Input Gate의 입력: 이전 output(h(t-1))과 현재 입력(x(t))
- Input Gate의 출력: C틸다 값과 i(t) element wise product가 일어나는데, 내가 지금 가지고 있는 cell state에 c(t)틸다 값을 얼마나 반영해줄지를 결정
- 정리: Forget과 Input Gate 모두 (이전 Cell state 값을 얼마나 버릴지)와 (현재 입력과 이전 출력으로 얻어지는 cell state candidate인 c(t) 틸다 값을 cell state 값에 얼마나 올리고 반영할지), 이 모든 것의 주체는 cell state임
3) Update


- Update, scaled by how much we decide to update
- input_gatecurr_state + forget_gateprev_state
- 이전 cell state를 forget gate로 얼마나 버릴지가 정해졌고, 거기에 얼마나 cell state를 업데이트를 정했으니 그 둘을 더해줌
4) Output Gate

- 최종적으로 얻어진 cell state의 값을 어떻게 밖으로 빼낼지
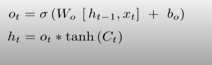
- -> 이 모든 것의 목적은 현재 입력과 이전 출력을 가지고 cell state에 어떻게 값을 집어넣고
이 cell state에 있는 값을 어떻게 빼줄지를 봄


- 정리: input(x(t))와 cell state와 hidden state가 들어가고 -> input gate, forget gate, output gate를 통과하여
-
cell state를 얼마나 업데이트하고 밖으로 빼낼지를 결정해주고 -> output이 나오면 다음번 cell state와 hidden state로 넘겨주는 것
- 여기서 4개의 뉴럴넷을 사용하는데 실제 사용할 때는 고려할 필요가 없음
실제 사용할 때는 입력과 출력을 정해주고 초기 cell state만 잘 초기화 시켜주면 tf나 pytorch에서 알아서 진행할 수 있음
In TensorFlow
lstm = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(num_units=n_neurons)
In Pytorch
import torch.nn as nn
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_class, hiddens_size=n_hidden, dropout=DROPOUT_RATE)
3. Pytorch 내의 Parameter 설명
1) Pytorch의 Parameter
- RNN/LSTM/GRU 각각의 cell은 모두 동일한 파라미터를 가짐
2) Pytorch Code
import torch.nn as nn
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers, bias=True, batch_first=True, dropout, bidirectional)
3) Parameters
- input_size: input의 feature dimension
- hidden_size: 내부에서 어떤 feature dimension으로 변경할 것인지
- num_layers: lstm layer를 얼마나 쌓을지
- bias: bias term 사용여부 (Default: True)
- batch_first: true면 batch_first=True면 [Batch_size, Seq_len, Hidden_size], flase면 [Seq_len,Batch_size,Hidden_size] (Default: False)
- dropout: 매 time step에서 layer에 적용, 가지치기
- bidirectional: 양방향 여부 true면 feature dimension 2배)
4) Inputs
Inputs: input,(h_0,c_0)
(1) input :

case1 배치 미사용:
(L, H(in))
(시퀀스 길이, 입력크기)
case2 배치 사용:
(N,L,H(in))
(배치사이즈, 시퀀스 길이, 입력 크기)
(2) h_0:
- initial hidden state
case1 배치 미사용:
(D*num_layers,H(out))
case2 배치 사용:
(D*num_layers,N,H(out))
(3) c_0:
- initial cell state
case1 배치 미사용:
(D*num_layers,H(cell))
case2 배치 사용:
(D*num_layers,N,H(cell))
5) outputs
Outputs: output,(h_n,c_n)
(1) output:
case1 배치 미사용:

(L, D*H(out))
case2 배치 사용:
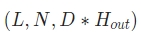
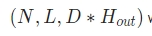
(L,N, DH(out)) or (N,L, DH(out))
(2) h_n:
case1 배치 미사용:

(D*num_layers,H(out))
case2 배치 사용:

(D*num_layers,N,H(out))
(3) c_n:
case1 배치 미사용:
(D*num_layers,H(cell))

case2 배치 사용:
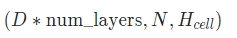
(D*num_layers,N,H(cell))
4. Pytorch LSTM 구현 튜토리얼




Referneces
1. Edwith 최성준 교수님의 논문으로 짚어보는 딥러닝의 맥
https://www.edwith.org/deeplearningchoi/lecture/15840?isDesc=false
2. 튜토리얼 자료
1) 유튜브 영상: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0_PgWWmauHk
2) 깃허브: https://github.com/python-engineer/pytorch-examples/blob/master/rnn-lstm-gru/main.py
Code:
https://github.com/python-engineer/pytorch-exampleshttps://github.com/python-engineer/py…
LSTM:
https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.LSTM.html

Leave a comment